| UPSC Relevance- Prelims Pointers River: Godavari State: Telangana Unique Feature: Largest multi-stage lift irrigation project in the world Key Barrages: Medigadda, Sundilla, Annaram, Ramadugu Main Controversy: Shift from Tummidihatti to Medigadda, structural failures, cost overrun Judicial Commission Head: Justice Pinaki Chandra Ghose Mains- GS PAPER-3– Infrastructure |
Why in News
- The piers of the Medigadda and Sundilla barrages in Telangana’s KLIP have developed cracks/sunk within just a few years of inauguration, raising concerns over engineering flaws and site selection.
- A one-man judicial commission headed by Justice Pinaki Chandra Ghose submitted its report (July 31, 2024) after probing alleged lapses, financial mismanagement, and hasty decisions in the project’s execution.
Telangana Government plans to discuss the findings in the State Legislature during the monsoon session
About the Project- (KLIP)
- The Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project is located on the Godavari River in Kaleshwaram, Bhupalpally, Telangana.
- It aims to provide water for irrigation and drinking to about 45 lakh acres in 20 districts of Telangana (excluding Hyderabad and Secunderabad).
- It is currently the world’s largest multi-stage lift irrigation project.
- The project’s source is the confluence of the Pranhita and Godavari rivers.
- The Pranhita River is formed by the joining of smaller rivers like Wardha, Painganga, and Wainganga, making it the seventh-largest drainage basin in the subcontinent.
- The project consists of seven sections and 28 packages, spanning over a distance of approximately 500 km (310 miles) across 13 districts.
- The canal network of the project stretches over 1,800 km (1,100 miles).
- The project plans to provide a total of 240 TMC (Thousand Million Cubic Feet) of water.
- The water will be used for irrigation, drinking water for nearby villages, municipal water supply to Hyderabad, and industrial use.
Controversies & Issues – KLIP
- Shift in Location – Planned at Tummidihatti, moved to Medigadda saying there was not enough water. Inquiry found water was actually available, making earlier ₹11,000 crore works at Tummidihatti useless.
- Poor Foundations – Barrages built on weak, water-permeable ground.
○ Sundilla piers sank within 3 years.
○ Annaram & Sundilla developed cracks due to storing excess water. - Unilateral Decision-making – Allegation that then CM KCR changed plans without Cabinet approval (BRS denies this).
- Cost & Funds Mismanagement – Project cost shot up, and funds were allegedly released carelessly without proper checks.
Way Forward
- Structural Rectification
○ Immediate technical audit by independent expert agencies (e.g., CWC, IITs) to assess foundation strength & repair needs. - Transparent Governance
○ Ensure Cabinet & Legislative approval before altering project scope/location in large infrastructure projects. - Cost & Time Monitoring
○ Strengthen third-party financial audits to prevent uncontrolled cost escalation. - Environmental Safeguards
○ Integrate river basin management plans; assess long-term sustainability considering climate change impacts. - Accountability Mechanisms
○ Fix responsibility for lapses; initiate disciplinary or legal action against negligent officials/contractors. - Public Disclosure
○ Make feasibility, hydrology, and design studies publicly available to build trust and prevent misinformation.
Conclusion
KLIP, meant to be Telangana’s lifeline, has been undermined by structural flaws, poor planning, and financial mismanagement. Restoring its utility and public trust requires urgent repairs, transparent governance, and strict accountability to prevent it from becoming a costly failure.
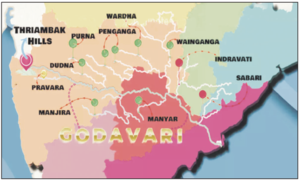
About Godavari River-
- Godavari is India’s second-longest river, often referred to as Dakshin Ganga (South Ganga).
- It originates from Trimbakeshwar in Maharashtra.
- The river flows 1,465 km eastward, passing through Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha.
- It finally drains into the Bay of Bengal.
- Major left-bank tributaries of the Godavari include Purna, Pranhita, Indravati, and Sabari.
- Major right-bank tributaries include Pravara, Manjira, and Manair.
Upsc prelims practice questions-
Q1. Which of the following statements about KLIP is correct?
- It is the world’s largest multi-stage lift irrigation project.
- It covers more than 16 lakh acres across Telangana.
- It is located at the confluence of the Krishna and Godavari rivers.
Select the correct answer:
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
Ans- A
Q2. Which of the following barrages are part of KLIP?
- Medigadda
- Sundilla
- Annaram
- Srisailam
Select the correct answer:
A. 1, 2, and 3 only
B. 1 and 4 only
C. 2, 3, and 4 only
D. 1, 2, 3, and 4
Ans- A – 1, 2, and 3 only
Medigadda, Sundilla, Annaram are KLIP barrages. Srisailam is on Krishna River, not part of KLIP.
Q3. The inquiry into KLIP lapses was led by:
A. Justice B.N. Srikrishna
B. Justice Pinaki Chandra Ghose
C. Justice Madan B. Lokur
D. Justice Kurian Joseph
B – Justice Pinaki Chandra Ghose
- Led the one-man judicial commission on KLIP lapses.
Q4. Consider the following statements regarding the Godavari River:
- Godavari is India’s second-longest river, often referred to as Dakshin Ganga.
- It originates from Trimbakeshwar in Maharashtra and drains into the Arabian Sea.
- The major left-bank tributaries of Godavari include Purna, Pranhita, Indravati, and Sabari.
- Major right-bank tributaries include Pravara, Manjira, and Manair.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 1, 3, and 4 only
B) 2 and 4 only
C) 1, 3, and 2 only
D) 1, 3, and 4
Answer: A) 1, 3, and 4 only
SOURCE- THE HINDU
Found this helpful?
Bookmark for revision, Practice the mains question, and
Share with fellow aspirants! THANK YOU
